Mesh_preprocessor_in_blender_with_python
 What does mesh preprocessor do in blender
What does mesh preprocessor do in blender
This project presents a mesh preprocessor tool which works with python and blender. It’s capable of processing mesh files in batch manner.
Introduction
The main reason to create such a mesh preprocessor is that preparing raw mesh files (especially .obj file format) for datasets usually is time-consuming, and it kind of needs tons of manual work. To free hands, a mesh processor tool is presented to do the dirty work for people.
Functions
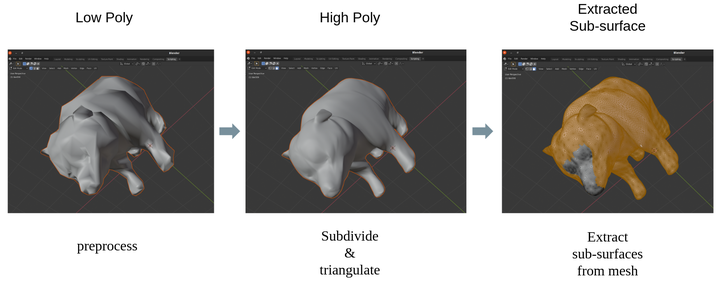
A few functions are added in this tool, for example, subdivide mesh into (or closest to) desired vertex number, triangulate the mesh if needed, and extract vertex indices of arbitrary sub-surfaces from the mesh.
Time consumption
For a computer with i7-6700k cpu and 16GB memory, it will take about ~3 hours when processing over 100 meshes (low poly) plus subdivding them into 50K vertices plus extracting 1K sub-surfaces for each mesh. It will take about ~9 hours when processing over 100 meshes (low poly) plus subdivding them into 150K vertices plus extracting 1K sub-surfaces for each mesh. The time consumption varies on the cpu and memory.
Inputs and Outputs
- inputs are mesh files ending with ‘.obj’, which are original mesh files you find or download online. In this repos, a folder named ‘data’ contains two examples.
- outputs are mesh files ending with ‘_tri.obj’ which are subdivided and triangulated mesh files, and data files ending with ‘.npy’ under corresponding “vertex_indinces_of_arbitrary_surfaces” which contains a list of numpy arrays of vertex indinces of sub-surfaces from each mesh.
Code
You can find the code in here.
Usage
- open blender software, if not installed, then download it from here. NO installation needed just unzip it.
- clone or download the zip file of this repos (then unzip it).
- click the “Scripting” tab on the above menu in blender, then click “Open” tab under “Scripting”, choose the work path to the mesh_preprocessor.py script in the unzipped repos.
- change the variable named “work_path” in the mesh_preprocesser.py.
- click the “Run Script” tab under “Scripting”, then you are ready to go. You can follow the steps to run script in blender as shown in the following image.
